Ever wondered how hackers hide their identities and stay anonymous while browsing the internet? It's no secret that they are a clever bunch; their methods of staying off the radar are one thing worth uncovering.
Hackers hide their identities by minimizing their digital footprints. They spoof their MAC addresses and use proxy servers or VPNs to conceal their IP addresses. They also avoid tracking search engines and use Tor for encrypted surfing, as well as browser fingerprint-blocking add-ons.
Contrary to popular belief, surfing the web anonymously isn't just for hackers. Anyone can benefit from learning how to do it correctly. We'll go over how exactly hackers hide their identities on the web and how you can use these same methods — so that you can surf the web anonymously and protect your identity and privacy like a pro.

Are You Free?
We are all too familiar with incessant ads that follow us around the web. Data companies can gather a lot of information about you from the web. They can tell which ads you should see based on all of the digital fingerprints you leave behind when you're online.
So, you are not free from being tracked by laissez-faire data companies.
Secondly, living in some countries where the government's eye is always watching may feel like an invisible prison. It can be difficult to express yourself freely without fear of dire consequences if you're traced back by authorities.
So, you are not free in oppressive regimes that actively censor their citizens' speech.
Also, have you ever been away from home and found yourself frustrated because you couldn't access your regular shows? Or have you had some websites blocked when you use certain Wi-Fi networks?
If yes, then you are not free from censorship protocols that limit what sites are available to you based on your location.
Freedom on the internet is an illusion; in reality, there are always eyes watching your online activity. To be free, you need to be anonymous. To be anonymous, need to keep your data traces hidden from others- just like hackers do.

Data Traces Are The Enemy Of The Anonymous
There is a famous hacker adage that goes: "If they haven't got your data, they can't catch you. "
Those who seek to emulate the anonymity of hackers online, must be aware that their data is often a traceable giveaway. They should be careful about the trails they leave behind when navigating the web. Some of the most common data traces include:
MAC address, IP address,
Browser fingerprints,
Cookies,
Insecure communication with HTTP
MAC Address
Every computer or smartphone that is capable of connecting to the internet or any local network has a device in it called a NIC (Network Interface Card). This device is given a permanent and unique 16-digit identifier by the manufacturer for identification.
This identifier is known as the MAC address. It has a format that looks like this: "aa-bb-cc-dd-ee-ff."
When a computer or smartphone attempts to connect to a local network, such as public Wi-Fi, it broadcasts its MAC address to the router or gateway, which will then be mapped to a corresponding IP address.
A MAC address can be a telltale sign of your identity because it can reveal who manufactured your device, and an ISP (Internet Service Provider) can store its customers' MAC addresses in its database. Also, since no two devices have the same MAC address, it can be used to track your activity.
For instance, when you are in a large area, such as an airport or city, with a unified Wi-Fi system, as you hop from one Wi-Fi spot to another. Your MAC address can be used to track your movements.
IP Address
An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a unique numerical label made of four-digit strings separated by periods (.), such as "192.124.33.1." It is assigned to each device connected to the Internet or any local networks (LAN), such as your home Wi-Fi.
An IP address is like a virtual postal code used to find a device's location on a network. This way devices can communicate with each other and know where to send or get data from. Internet-connected devices have public IP addresses, while LAN-connected devices have private IP addresses.
An IP address is another rich data trace you leave behind that might expose your location. Also, any website server can log or retain visitors' IP addresses and match them to the actions performed.

Browser Fingerprints
Browser fingerprinting is a tracking technique that can identify individual users based on the unique attributes of the person's web browser.
Browser fingerprinting relies on features such as installed fonts, IP address, device type, add-ons, and operational system to create a "digital identity" of a user that can be used to track their online activities without the user knowing it is happening.
Cookies
Unbeknownst to many, Facebook (Meta) can track people's web activity and link it to their individual Meta accounts or create a data set for individuals who are not (yet) members of Meta. Arnold's paper "Facebook Tracks and Traces Everyone: Like This" reveals that major corporations' tentacles extend far and beyond.
The Meta " like" button embedded on a website is a third party cookie. But wait, what exactly is a cookie?
A cookie is a small text file containing information that is sent to your browser when you visit a website. It can track your browsing activity and store it in the form of text files which are then relayed back to the web server each time you revisit the website.
So, if you were to visit Amazon and log into your account, Amazon would store your browsing history and preferences as a cookie, so the next time you revisit, the site will recognize you and your preferences will already be applied.
A third party cookie, by definition, is a cookie that is fed to your browser by a website which is different from the one you’re currently visiting.
In the case of Meta, this means that if you happen to visit a website with an embedded ‘like’ button, Meta will be able to store data about your browsing behavior, such as links you clicked on or even how long you stayed on a certain webpage. These data are then used to generate an individual profile of your online behavior which can be later used for targeted advertising.
Although cookies serve beneficial purposes, users are unaware of the various tracking techniques employed by companies and thus have no control over their data.
HTTP Protocol (Insecure Communication)
Visiting websites that are still using the HTTP protocol instead of HTTPS can be detrimental to your privacy and security.
An HTTP connection is an unencrypted one, which means that all data sent back and forth between you and the website is visible in plain text to anyone who happens to intercept the communication.
Governments, ISPs, or any other 'eavesdroppers' on the web have free reign over this unencrypted information… Check out Mike's in-depth article on how to protect your encrypted data.
Hackers understand how data trails enable authorities to identify and track users. Thus they have developed a range of techniques for concealing these fingerprints - allowing them to move undetected by law enforcement. If you want more control over your online security level too, here are some useful methods that you can start putting in practice right away:

How Hackers Hide Their MAC Addresses?
Hiding or masking your device's real MAC address is called MAC address spoofing. This means that you can disguise your device's real address with a fake one. The way to mask a MAC address depends on the system you are using.
Check out this article for instructions on how to do it in Windows 10, macOS, Android, and iOS systems.
How Hackers Hide Their IP Addresses?
Hackers hide their IP addresses by using using proxy servers or by using VPNs.
Proxy server
A proxy server is a middeman between your computer and the server or another computer on the Internet. It takes all the information that you sent out and it routes it through a different IP address so servers or other computers that are communicating with your device see the IP address of the proxy server and not yours.
Here is a list of web proxies that don't require any configuration. They allow you to directly navigate the web anonymously:
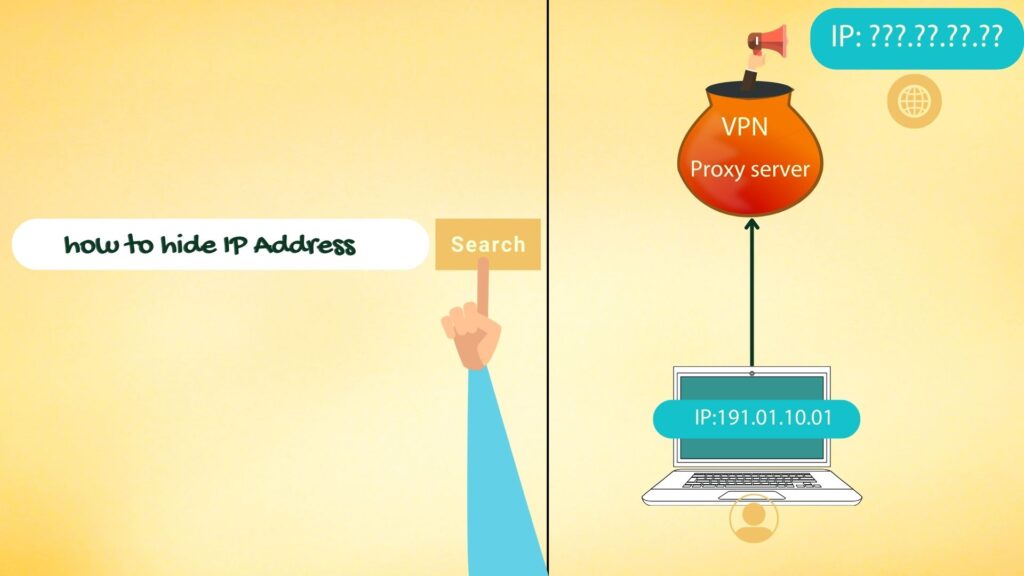
VPN (Virtual Private Network)
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, is an encrypted connection that provides security and privacy over public networks like the Internet.
It creates an encrypted tunnel between your device and another server. All the data that goes through this tunnel—and all requests sent out from your device—are encrypted, meaning that anyone snooping on the connection won’t be able to understand what’s being communicated.
Here is a list of VPN that can use:
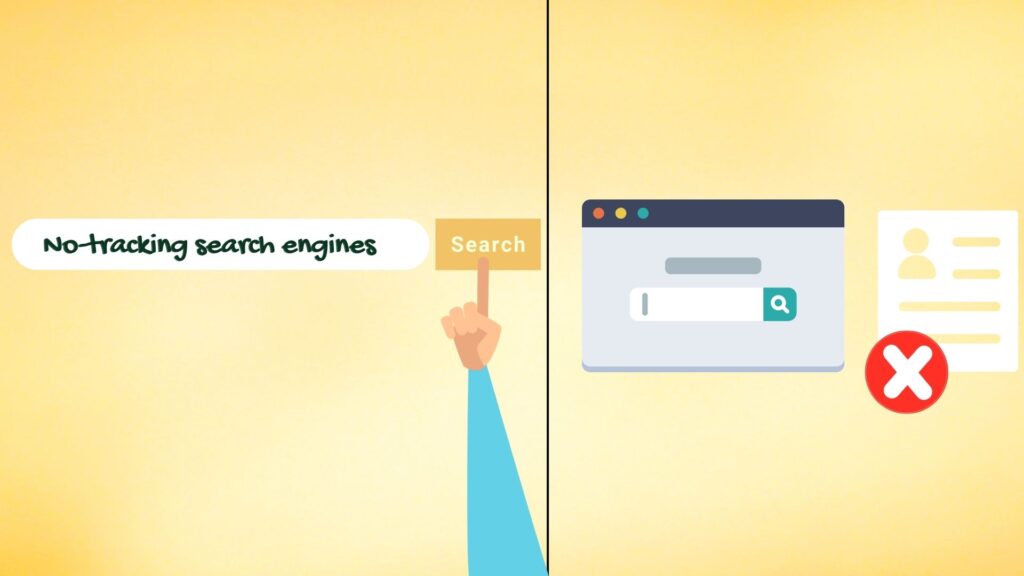
Hackers Hide By Using No-Tracking Search Engines
No-tracking search engines are the future of privacy.
Google is the most popular search engine in the world, with a market share of around 83% according to Statista. However, it is also an advertising company, and as such, it is also notorious for tracking and storing user data. To Google, you are essentially the product.
If you are uncomfortable with this level of surveillance, no-tracking search engines like, Brave and DuckDuckGo can help protect your privacy. Both of these services offer a Google-style search experience with the added benefit of not tracking any user data or activity.
Thus, if you want to stay anonymous online, ditch Google and use one of these search engines that doesn't track you.
Hackers Hide By Using Tor Network
You may have heard of the term "Tor network" in conversations or news stories related to cyber security and hacking. But what is a Tor network, exactly?
In simple terms, the Tor network is sometimes called "onion routing," and it works by bouncing your data through multiple computers around the world before reaching its destination- making it very very difficult for anyone monitoring your activity to trace back to your origin point.
There are many reasons for using Tor as a browser. It isolates each website you visit so trackers and ads can't follow you, while also clearing cookies and browsing history.
Tor also masks the user's IP address, meaning it's impossible for websites or other entities to detect their precise geographic location.
In addition, Tor makes every user look the same through its network, rendering it virtually impossible to be identified by their browser and system information.
Furthermore, this anonymity allows users to bypass censorship restrictions imposed by their home networks and access blocked websites.

Hackers Hide By Controlling Cookies
You can browse in incognito mode. Most browsers offer private browsing. It temporarily disables anonymity-compromising features such as cookies, history, cache, temporary files, sessions, and saved password. You can also use a cookie manager extension add-on like Ghostery.
You can also manually delete cookies frequently through your browser’s settings. This ensures cookies stored by websites are periodically deleted.
Either way, taking control of your browser's cookies is an excellent approach to boost your anonymity and privacy, just like hackers do.
Hackers Hide By Using Extensions That Stop Browser Fingerprinting
Anonymous access is one of the internet's founding principles, and I'm sure you and I, like many others, prefer privacy over marketing or ad personalization techniques that come with giving away data.
Hence, I and others consider browser fingerprinting to be an intrusive method. It gathers information about you without your knowledge or consent. Browser fingerprinting allows you to be tracked for months, even when you clear your browser storage or use private browsing mode — disregarding your clear indications that you don’t want to be tracked.
Fortunately, there are ways to protect yourself from browser fingerprinting. You can use extensions like Canvas Blocker. Also, browsers like Mozilla have adopted 'fingerprint blocking' as the default setting to stop third-party requests from companies that are known to engage in fingerprinting.

Hackers Hide By Using Steganography
Steganography is a practice that has been used for centuries to hide information in plain sight. It can be used to hide data or messages within a file, image, or any other digital asset.
Steganography has become an ineffective tool for hackers to discreetly transfer secret messages without triggering suspicion.
If you have a secret message that contains sensitive information, it can be embedded in a picture or audio file and sent without raising suspicion using steganography.
Here are some of the free tools available to encrypt and decrypt messages with steganography:
Final Thoughts
This article is not intended to teach or encourage illegal activity, but by understanding how hackers protect themselves online and implementing similar methods, you can take back control of your privacy and security.
If you want to learn more about how to protect your privacy online, Jess Stratton can help. She's teaching a course on LinkedIn called Learning Computer Security and Internet Safety.
Don't let others track you, identify you or steal your data — use these methods to keep yourself anonymous, safe and secure online.